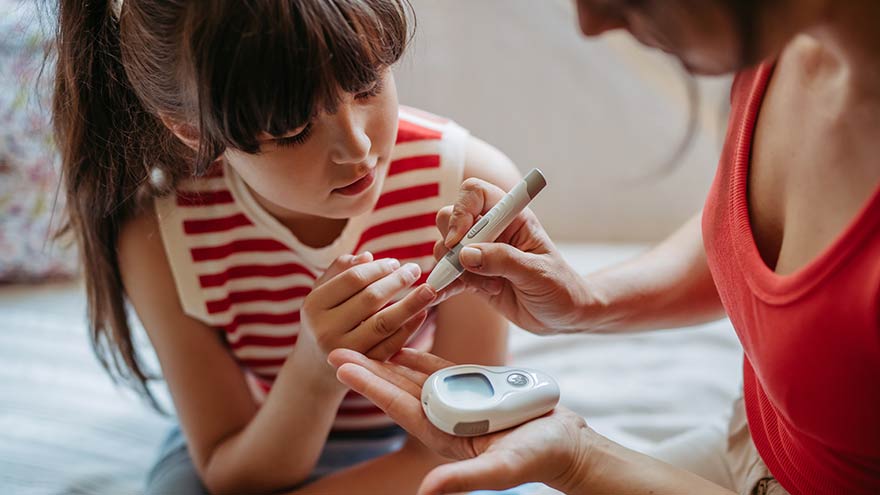
Maintaining a balanced diet is crucial for overall health and well-being. One of the fundamental aspects to consider is how food choices impact blood sugar levels. Understanding and managing these levels are essential, particularly for individuals with diabetes or those at risk of developing the condition.
The Connection Between Diet and Blood Sugar Levels
Blood sugar, or glucose, is the primary energy source for the body’s cells. It is derived from the foods we consume, especially carbohydrates. When we eat, our digestive system breaks down these carbohydrates into glucose, which then enters the bloodstream. The pancreas releases insulin, a hormone that helps cells absorb glucose to be used for energy or stored for future use. However, the type of food you eat can significantly affect this process and, consequently, your blood sugar levels.
Processed foods, high in refined sugars and simple carbohydrates, can cause rapid spikes in blood sugar levels. On the other hand, consuming complex carbohydrates, fiber-rich foods, and lean proteins contribute to a more gradual and sustained release of glucose into the bloodstream. This balance helps maintain stable energy levels and reduces the risk of sugar crashes that can trigger cravings and overeating.
Importance of Complex Carbohydrates and Fiber
Incorporating complex carbohydrates and fiber into your diet is imperative for maintaining sugar balance. Unlike simple carbohydrates, which are quickly digested and absorbed, complex carbohydrates provide a more sustained energy release. Foods rich in fiber, such as whole grains, legumes, vegetables, and fruits, slow down the digestion process and help regulate blood sugar levels.

Proteins and Healthy Fats: Vital Allies for Sugar Balance
Proteins and healthy fats play a significant role in stabilizing blood glucose levels. Protein-rich foods, such as lean meats, fish, eggs, dairy products, and plant-based proteins, are digested more slowly than carbohydrates. This slow digestion helps maintain steady blood sugar levels and keeps you feeling full for longer periods.
Healthy fats, found in avocados, nuts, seeds, and olive oil, also contribute to sugar balance by slowing the absorption of carbohydrates. Including these fats in your meals can prevent the rapid spike in blood sugar levels that often follows the consumption of high-carb meals. By incorporating balanced amounts of proteins and healthy fats into your diet, you can mitigate blood sugar fluctuations and maintain a more stable energy level throughout the day.
The Role of Portion Control and Meal Timing
Beyond food choice, portion control and meal timing are essential factors in managing blood sugar levels effectively. Overeating, even healthy foods, can lead to increased blood glucose levels. Practicing portion control ensures that you consume appropriate amounts of each food group, preventing excessive calorie intake and subsequent spikes in blood sugar.
Lifestyle Changes for Sustainable Sugar Balance
Achieving and maintaining a balance sugar level goes beyond dietary choices. Incorporating regular physical activity into your routine can significantly impact blood sugar regulation. Exercise improves insulin sensitivity, enabling cells to use glucose more efficiently. Aiming for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, can have profound effects on your overall health.
Additionally, health service stress management and adequate sleep are integral to maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Chronic stress and sleep deprivation can disrupt hormonal balance and affect glucose metabolism. Practices such as mindfulness, yoga, and ensuring 7-9 hours of quality sleep per night can contribute to better sugar balance and overall well-being.
In conclusion, making informed dietary choices, practicing portion control, being mindful of meal timing, and adopting a healthy lifestyle are fundamental steps to achieve better balance. Prioritizing complex carbohydrates, fiber, proteins, and healthy fats, along with regular physical activity and stress management, can help maintain stable blood sugar levels and improve long-term health outcomes.